
By Jonathan Saul, Noah Browning and Mohammed Ghobari
LONDON/DUBAI (Reuters) – Intensive care wards in Yemen’s hospitals are filled with emaciated children hooked up to monitors and drips – victims of food shortages that could get even worse due to a reorganization of the central bank that is worrying importers.
With food ships finding it hard to get into Yemen’s ports due to a virtual blockade by the Saudi-led coalition that has backed the government during an 18-month civil war, over half the country’s 28 million people already do not have enough to eat, according to the United Nations.
Yemen’s exiled president, Abd Rabbuh Mansur Hadi, last month ordered the central bank’s headquarters to be moved from the capital Sanaa, controlled by Houthi rebels in the north, to the southern port of Aden, which is held by the government. He also appointed a new governor, a member of his government who has said the bank has no money.
Trade sources involved in importing food to the Arab peninsula’s poorest country say this decision will leave them financially exposed and make it harder to bring in supplies.
Diplomats and aid officials believe the crisis surrounding the central bank could adversely affect ordinary Yemenis.
“The politicization of the central bank and attempts by the parties in the conflict to use it as a tool to hurt one another … threaten to push the poorest over the edge,” said Richard Stanforth, humanitarian policy adviser with Oxfam.
“Everything is stacked against the people on the brink of starvation in Yemen.”
The effects of food shortages can already be seen. At the children’s emergency unit at the Thawra hospital in the port of Hodaida, tiny patients with skin sagging over their bones writhe in beds. Hallways and waiting rooms are crowded with parents seeking help for their hungry and dying children.
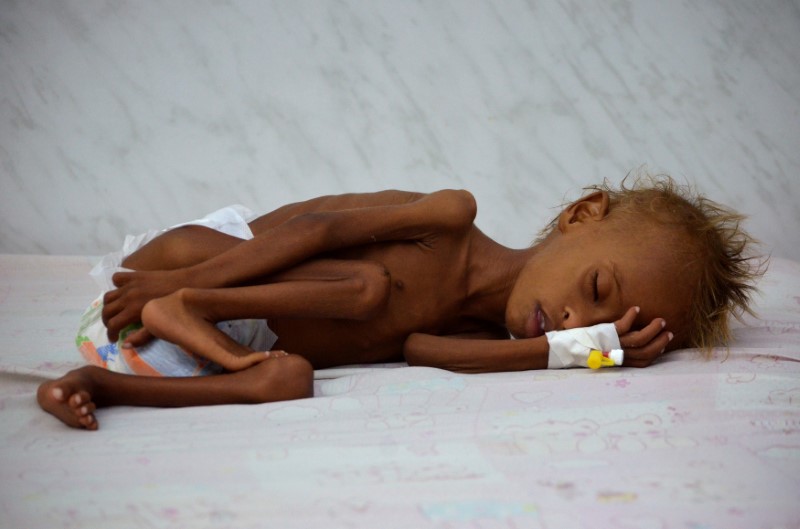
Salem Abdullah Musabih, 6, lies on a bed at a malnutrition intensive care unit at a hospital in the Red Sea port city of Hodaida, Yemen September 11, 2016. REUTERS/Abduljabbar Zeyad
Salem Issa, 6, rests his stick-thin limbs on a hospital bed as his mother watches over him. “I have a sick child, I used to feed him biscuits, but he’s sick, he won’t eat,” she said.
A nurse said the ward began taking in around 10 to 20 cases in April, but now struggles with 120 patients per month.
The World Food Programme says half Yemen’s children under five are stunted, meaning they are too short for their age because of chronic malnutrition.
IMPORTERS STRUGGLING
In July, Reuters reported that importers were already struggling to buy food from abroad because $260 million worth of their funds were frozen in Yemeni banks, while Western banks had cut credit lines.
Since then, importers have guaranteed much of the risk of financing shipments themselves.
The decision to move the central bank, seen as the last impartial bastion of the country’s financial system which has helped keep the economy afloat in wartime, is viewed as a major blow for suppliers who are mistrustful of the decision and expect even more chaos ahead. Foreign exchange is already scarce and the sources do not have confidence in the new governor.
All of this will lead to further food disruptions and more hardship for Yemenis already facing impending famine, according to the trade sources.
“We have begun to cancel our forward contracts – it’s just impossible to trade when there is no financial system in place. There is no coverage from the central bank where we can trust them or know them,” said one source.
“This leaves anyone bringing in cargoes completely exposed,” added the source, who declined to be identified due to the worsening security situation and fear of reprisals.
Shipping data showed at least nine vessels carrying supplies such as wheat and sugar were on the way to the Yemeni ports of Hodaida and Salif, but the source said there were worries for forward shipments for late October and November.
A second trade source also active in Yemen confirmed the growing difficulties.
“Western banks are not willing to process payments and the whole system is freezing up. It is an ever growing struggle to do anything commercial,” the second source said.
“Obtaining foreign exchange has to be done through currency smuggling. Yemen is like a country of smugglers now – this is unacceptable.”

A woman holds her child at the door of her hut in al-Tuhaita district of the Red Sea province of Hodaida, Yemen September 26, 2016. REUTERS/Abduljabbar Zeyad
DWINDLING RESERVES
The old central bank in the capital Sanaa used Yemen’s dwindling foreign exchange reserves to guarantee shipments into a country which imports 90 percent of its food.
But Hadi disliked the bank paying salaries to his foes in the army and the Iran-aligned Houthi movement opposed to his internationally recognized government.
Struggling to advance on the battlefield and keen to undermine the Houthis, Hadi dismissed the bank’s governor, Mohamed Bin Humam, named Finance Minister Monasser Al Quaiti in his place and decreed the bank be moved to Aden.
It was a sudden decision that aroused suspicion among traders.
“The governor Humam enjoyed the confidence of all parties since he was clearly independent and working in the best interests of Yemen. To now appoint a minister of finance of the government is a retrograde step and none of the traders have any confidence in him or in the bank in Aden,” the first trade source said.
The new governor of the central bank did not immediately respond to a Reuters request for comment.
Quaiti told the Saudi-owned Asharq al-Awsat newspaper on Thursday he had inherited a bank with no money, but he pledged to keep it independent.
Ibrahim Mahmoud, of Yemen’s Social Development Fund, said only an improvement in the country’s financial system and an emergency aid effort could stop the spread of hunger.
“If there is no direct and immediate intervention on behalf of the international community and state organizations, we could be threatened by famine and a humanitarian catastrophe.”
Even though moving the central bank seemed to be aimed at hurting the Houthis, Yemeni economic officials and diplomats say the group has its own financial resources.
Losing out on $100 million in salaries to its fighters as suggested by the new bank governor may hurt the Houthis, but the bank’s closure in Sanaa is likely to hurt ordinary people already suffering from a collapse in the economy due to the war.
“It risks leaving the salaries of more than a million Yemenis unpaid. There may be a long-term effect on the Houthis, but the immediate effect will be on normal people trying to put food on the table,” Yemeni economic analyst Amal Nasser said.
(Additional reporting by Michael Hogan in Hamburg, Stephanie Nebehay in Geneva; Editing by Giles Elgood)

 Egypt’s foreign currency reserves took a major hit in January falling 10%.
Egypt’s foreign currency reserves took a major hit in January falling 10%.

