By Brian Thevenot
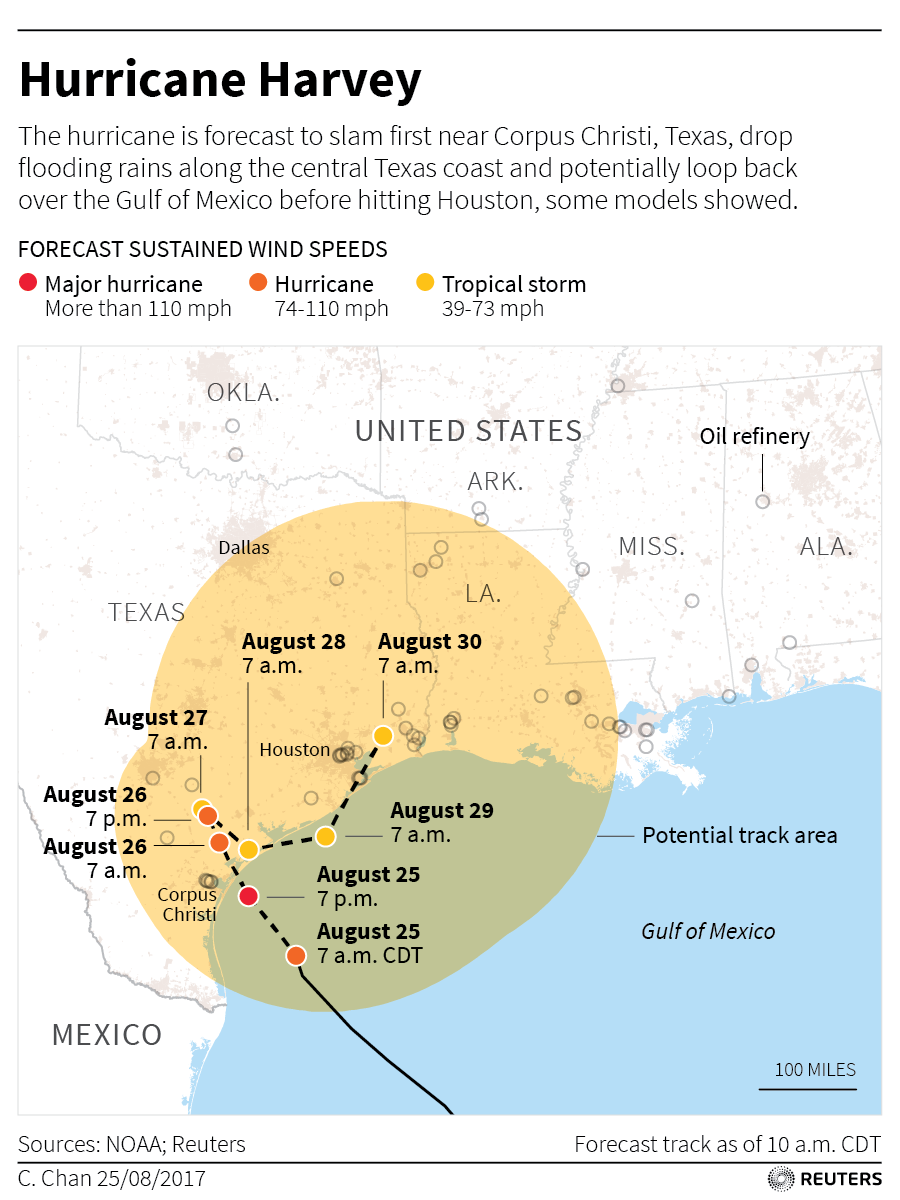
CORPUS CHRISTI, Texas (Reuters) – The most powerful hurricane to hit the U.S. state of Texas in more than 50 years moved slowly inland on Saturday, dumping torrential rain expected to cause catastrophic flooding after battering the coast with 130 miles per hour winds.
Texas utility companies said nearly a quarter of a million customers were without power. Residents and emergency respondents were still sheltering from the storm early on Saturday, making it difficult to gauge the full extent of the damage.
Harvey is the strongest storm to hit Texas, the center of the U.S. oil and gas industry, since 1961.
For a graphic on Hurricanes in the North Atlantic, click http://tmsnrt.rs/2gcckz5
The town of Rockport, 30 miles (48 km) north of the city of Corpus Christi, appeared to be one of the hardest hit. Ahead of the storm’s arrival, the city’s mayor told anyone staying behind to write their names on their arms for identification purposes in case of death or injury.
“Right now we’re still hunkered down and can’t go anywhere,” Steve Sims, the volunteer fire chief in Rockport, said early on Saturday.
“We’ve heard rumors of 1,000 different things, we can’t confirm anything because we haven’t seen anything. We know we’ve got a lot of problems, but we don’t know what yet.”
A high school, hotel, senior housing complex and other buildings suffered structural damage, according to emergency officials and local media. Some were being used as shelters.
Sims said power, internet and most cell phone service was out in the town of 10,000 where about two-thirds of residents evacuated. Most of the senior citizens and nursing homes were among the first to be evacuated, he said.
The hurricane came ashore northeast of the city of Corpus Christi late on Friday with maximum winds of 130 miles per hour (209 km per hour). That made it a Category 4 storm on the Saffir-Simpson scale, the second-highest category and the most powerful storm in over a decade to hit the mainland United States.
The streets of Corpus Christi, which has around 320,000 residents, were deserted early on Saturday, with billboards twisted and damaged and strong winds still blowing.
City authorities asked residents to reduce use of toilets and faucets on Saturday because power outages left waste water plants unable to treat sewage.
The city also asked residents to boil water before consumption.
A drill ship broke free of its mooring overnight and rammed into some tugs in the port of Corpus Christi, port executive Sean Strawbridge said. The crews on the tugs were safe, he added.
The city was under voluntary evacuation ahead of the storm.
HEADING INLAND, STORM WEAKENS
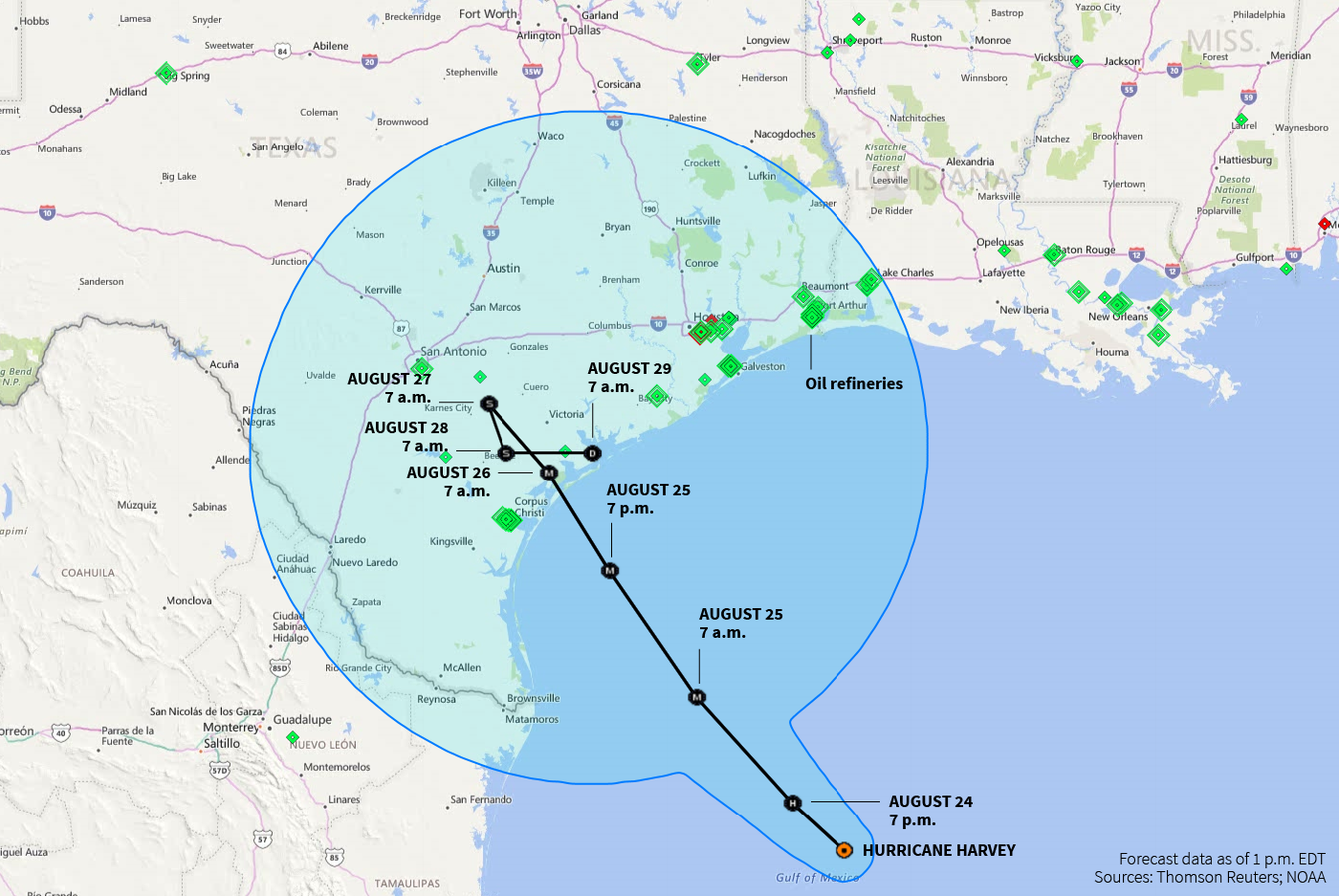
The storm weakened to Category 1 early on Saturday and was expected to be downgraded to a tropical storm later in the day, the U.S. National Hurricane Center said. Harvey was about 125 miles (201 km) southwest of Houston, moving at about six mph (10 km per hour), the center said.
Harvey was expected to linger for days over Texas and bring as much as 40 inches (101.6 cm) of rain to some parts of the state.
The latest forecast storm track has Harvey making a loop, heading back toward the Gulf of Mexico coast, and then turning north again on Tuesday. (http://tmsnrt.rs/2g9jZ0W)
Nearly 10 inches of rain had already fallen in a few areas in southeastern Texas, the center said. Flash floods have already hit some areas, the National Weather Service said.
As many as 6 million people were believed to be in Harvey’s path, as is the heart of America’s oil-refining operations. The storm’s impact on refineries has already pushed up gasoline prices. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency eased rules on gasoline specifications late on Friday to reduce shortages.
U.S. President Donald Trump, facing the first big natural disaster of his term, said on Twitter he signed a disaster proclamation which “unleashes the full force of government help” shortly before Harvey made landfall.
“You are doing a great job – the world is watching” Trump said on Saturday in a tweet referring to the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), which coordinates the response to major disasters.
One Corpus Christi resident, Donna McClure, said on Twitter before the storm made landfall: “In the dark, internet out, ham radio not working. Is anybody out there? Alone trying not to be scared.”
Utilities American Electric Power and CenterPoint Energy reported a combined total of more than 240,000 customers without power.
While thousands fled the expected devastating flooding and destruction, many residents stayed put in imperiled towns and stocked up on food, fuel and sandbags.
HOUSTON PREPARES FOR FLOODS
Harvey was the first major hurricane of Category 3 or more to hit the mainland United States since Hurricane Wilma struck Florida in 2005.
Its size and strength also dredged up memories of Katrina, the 2005 hurricane that made a direct hit on New Orleans as a Category 3 storm, causing levees and flood walls to fail in dozens of places. About 1,800 died in the disaster made worse by a slow government emergency response.
Texas and Louisiana declared states of disaster before Harvey hit, authorizing the use of state resources to prepare.
Residents of Houston, the nation’s fourth most populous city, were woken with automatic flash flood warnings to their cell phones early on Saturday.
The city warned residents of flooding from close to 20 inches (60 cm) of rain over several days.
GASOLINE PRICES SPIKE
Gasoline stations on the south Texas coast were running out of fuel as residents fled the region. U.S. gasoline prices spiked as the storm shut down several refineries and 22 percent of Gulf of Mexico oil production, according to the U.S. government.
More than 45 percent of the country’s refining capacity is along the U.S. Gulf Coast, and nearly a fifth of the nation’s crude oil is produced offshore.
Ports from Corpus Christi to Texas City, Texas, were closed to incoming vessels and Royal Dutch Shell Plc, Anadarko Petroleum Corp, Exxon Mobil Corp and others have evacuated staff from offshore oil and gas platforms.
Concern that Harvey could cause shortages in fuel supply drove benchmark gasoline prices to their highest level in four months. Profit margins for making gasoline hit their strongest levels in five years for this time of year.
The U.S. government said it would make emergency stockpiles of crude available if needed to plug disruptions. It has regularly used them to dampen the impact of previous storms on energy supplies.
(Reporting by Brian Thevenot; Additional reporting by Jessica Resnick-Ault in New York and Liz Hampton and Ernest Scheyder in Texas; Writing by Brendan O’Brien and Simon Webb; Editing by Helen Popper and Matthew Lewis)