By Maureen N. Maratita and Christine Kim
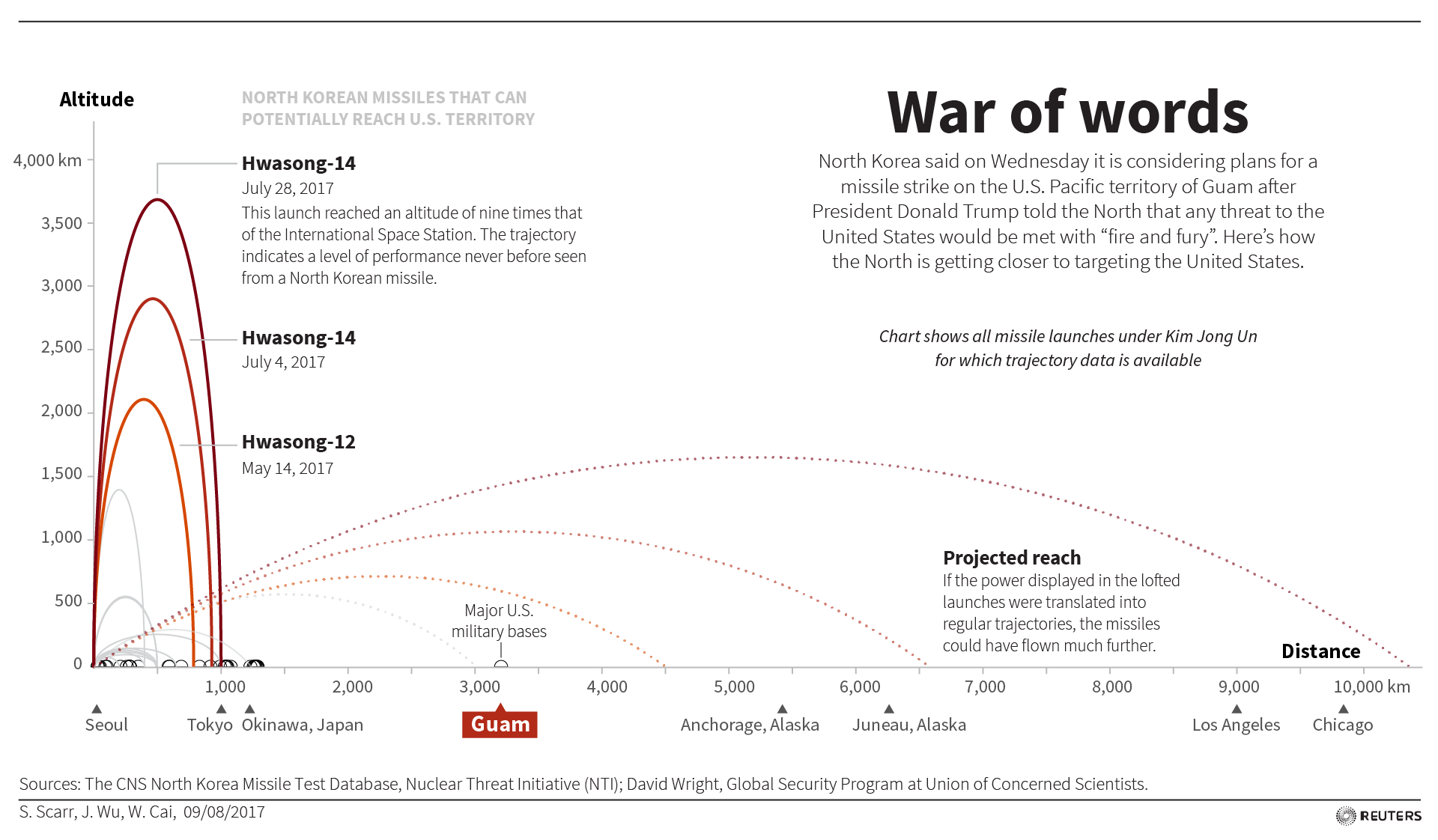
GUAM/SEOUL (Reuters) – North Korea said on Wednesday it is considering plans for a missile strike on the U.S. Pacific territory of Guam, just hours after President Donald Trump told the North that any threat to the United States would be met with “fire and fury”.
The sharp increase in tensions rattled financial markets and prompted warnings from U.S. officials and analysts not to engage in rhetorical slanging matches with North Korea, which regularly threatens to destroy the United States.
North Korea said it was “carefully examining” a plan to strike Guam, which is home to about 163,000 people and a U.S. military base that includes a submarine squadron, an airbase and a Coast Guard group.
A Korean People’s Army spokesman said in a statement carried by state-run KCNA news agency the plan would be put into practice at any moment, once leader Kim Jong Un made a decision.
Guam Governor Eddie Calvo dismissed the threat and said the island was prepared for “any eventuality” with strategically placed defenses. He said he had been in touch with the White House and there was no change in the threat level.
“Guam is American soil … We are not just a military installation,” Calvo said in an online video message.
North Korea, which is pursuing missile and nuclear weapons programs in defiance of U.N. Security Council resolutions, also accused the United States of devising a “preventive war” and said in another statement that any plans to execute this would be met with an “all-out war, wiping out all the strongholds of enemies, including the U.S. mainland”.
Washington has warned it is ready to use force if needed to stop North Korea’s ballistic missile and nuclear programs but that it prefers global diplomatic action, including sanctions. The U.N. Security Council unanimously imposed new sanctions on North Korea on Saturday.
Trump issued his strongest warning yet for North Korea in comments to reporters in New Jersey on Tuesday.
“North Korea best not make any more threats to the United States. They will be met with fire and fury like the world has never seen,” Trump said.
U.S. Secretary of State Rex Tillerson, before landing in Guam on a pre-arranged visit, said Trump was trying to send a strong message.
“So I think the president, what the president is doing, is sending a strong message to North Korea in language that Kim Jong Un would understand, because he doesn’t seem to understand diplomatic language,” Tillerson told reporters.
Just moments after Tillerson’s remarks were reported, Trump hammered home his tough talk in a Twitter post about the U.S. nuclear arsenal, in what looked like another warning to North Korea.
“My first order as President was to renovate and modernize our nuclear arsenal,” he said. “It is now far stronger and more powerful than ever before.”
China, North Korea’s closest ally despite Beijing’s anger at Pyongyang’s missile and nuclear programs, described the situation as “complex and sensitive”, and urged calm and a return to talks.
“China calls on all sides to uphold the main direction of a political resolution to the Korean peninsula nuclear issue, and avoid any words or actions that may intensify the problem and escalate the situation,” it said in a statement sent to Reuters, repeating its customary stance.
“‘BLACK SWAN’ EVENT”
North Korea has made no secret of its plans to develop a nuclear-tipped missile able to strike the United States and has ignored all calls to halt its weapons programs.
Pyongyang says its intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) are a legitimate means of defense against perceived U.S. hostility, including joint military drills with South Korea.
The standoff drove investors out of stocks on Wednesday and into the safety of the yen, Swiss franc, gold and government debt. South Korea’s benchmark index <.KS11> and Japan’s Nikkei <.N225> both closed down more than 1 percent. [MKTS/GLOB]
“Tensions will continue to mount and could eventually develop into a ‘black swan’ event that the markets are not prudently considering,” Steve Hanke, professor of Applied Economics at Johns Hopkins University, told the Reuters Global Markets Forum.
South Korea and the United States remain technically still at war with North Korea after the 1950-53 Korean conflict ended with a truce, not a peace treaty.
The South Korean capital, Seoul, is home to roughly 10 million people and within range of massed North Korean rockets and artillery, which would be impossible to destroy in a first U.S. strike.
Tens of thousands of U.S. troops remain stationed in South Korea and in nearby Japan, the only country to have been attacked with nuclear weapons. Wednesday marked the 72nd anniversary of the atomic bombing of the city of Nagasaki by the United States.
“WAR, WAR, WAR”
A senior official at South Korea’s presidential Blue House rejected talk of a crisis on the Korean peninsula, saying Seoul saw a high possibility of resolving the issue peacefully.
North Korea needed to realize its provocations are making the country more isolated and it should respond to the South’s proposal for dialogue, the official said.
In Dandong, a Chinese trading hub across the border from North Korea, residents said they were unperturbed by the escalating rhetoric.
“North Korea always talks about war, war, war, but it never happens,” said a restaurant owner who asked to be identified only by her surname, Yang.
“We now live in peaceful times. But if war does break out it will be us ordinary people that suffer.”
Tension in the region has risen since North Korea carried out two nuclear bomb tests last year and two ICBM tests in July.
Japanese fighters conducted joint air drills with U.S. supersonic bombers in Japanese skies close to the Korean peninsula on Tuesday, Japan’s Air Self Defence Force said.
On Monday, two U.S. B-1 bombers flew from Guam over the Korean peninsula as part of its “continuous bomber presence”, a U.S. official said, in a sign of the island’s strategic importance.
DEEPLY TROUBLING
Guam, popular with Japanese and South Korean tourists, is protected by the advanced U.S. Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) anti-missile system, deployed in South Korea.
“I know they’ve not been successful,” Vilma Quichocho, a treasurer at Guam’s Department of Administration, said of previous attempts to launch missiles from North Korea. “But now they’re talking about nuclear warheads and it’s kind of scary.”
Madeleine Z. Bordallo, the U.S. Congresswoman for Guam, said she was confident U.S. forces could protect it from the “deeply troubling” North Korean nuclear threat. She called on Trump to show “steady leadership” and work with the international community to lower tension.
Seoul resident Kim Sung-un, 29, said North Korea tended to make a lot of threats about missile attacks, but did not follow through.
“So I am leaning toward going to Guam, but also at the same time, I can’t help feeling anxious about it,” she said.
Republican U.S. Senator John McCain said Trump should tread cautiously when issuing threats, unless he is prepared to act.
“I take exception to the president’s comments because you’ve got to be sure you can do what you say you’re going to do,” he said in a radio interview.
Former U.S. diplomat Douglas Paal, now with the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace think tank in Washington, said Trump should not get into a war of words with Pyongyang.
“It strikes me as an amateurish reflection of a belief that we should give as we get rhetorically. That might be satisfying at one level, but it takes us down into the mud that we should let Pyongyang enjoy alone,” said Paal, who served as a White House official under previous Republican administrations.
In a small show of goodwill, North Korea said on Wednesday it had released a Canadian pastor serving a life sentence there on humanitarian grounds.
There was no obvious direct connection between the release and the standoff with the United States, but North Korea has in the past attracted the attention of Washington, and visits by high-profile Americans, with the detention and release of U.S. citizens.
(Additional reporting by Soyoung Kim in SEOUL, Amy Miyazaki, Linda Sieg and Tim Kelly in TOKYO, Philip Wen in DANDONG, Martin Petty in MANILA, James Oliphant, Doina Chiacu, Susan Heavey, John Walcott, Idrees Ali and David Brunnstrom in WASHINGTON, Rodrigo Campos in NEW YORK, and Divya Chowdhury in MUMBAI; Writing by Lincoln Feast; Editing by Paul Tait and Nick Macfie)